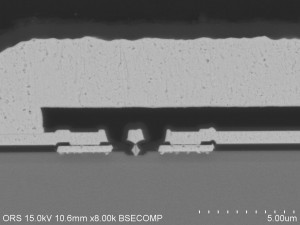
Construction Analysis
Testing Options
- Ball Shear Strength
- Bond Strength
- DC I.V. Curve Tracing
- Die Shear Strength
- Digital Microscopy
- External Visual Inspection
- Fluorescence Microscopy
- Glassivation Layer Integrity
- High Resolution Film X-ray
- Internal Visual Inspection
- Micro Cross-Sectioning
- Nitric and Sulfuric Decapsulation
- Particle Impact Noise Detection
- SEM Metallization Inspection
- Solder Reflow/Moisture Sensitivity Testing
- Sub-micron Real Time X-ray
- Die Back Metallization
- Glassivation Thickness
- Metallization Thickness
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Inspection
- Via Metallization
- Wafer Thickness
- C-SAM
- Hermeticity Testing
- Dye Impregnation
- Elemental Analysis
Construction Analysis is a customized sequence of applicable analytical techniques to evaluate the inherent design and robustness of a component or assembly. A well-executed Construction Analysis examines and documents the physical characteristics including material elemental composition, dimensions and quality details of the assembly. This testing methodology was originally created to assess commercial electronic components, i.e. plastic non-hermetic packages, but can be applied to virtually any manufactured product. Each analysis employs a series of non-destructive and destructive tests appropriate for the product type.
Construction Analysis may be used to assess the overall quality and workmanship of a component, this service can effectively be used to;
- Identify and monitor process changes.
- Identify deviations from contractual requirements.
- Benchmark your product relative to your competitor’s product.
- Identify anomalies/defects and possible causes and ramifications.
A typical Construction Analysis program involves;
For Packaging Analysis
- External Visual Inspection: to assess overall exterior quality and workmanship and dimensional analysis.
- Real Time X-Ray Inspection: to non-destructively detect internal defects with void analysis.
- Particle Impact Noise Detection: to detect loose particles inside a device cavity.
- Acoustic Microscopy (SAM): to non-destructively assess quality of construction material adhesion at interfaces.
- Hermeticity and Internal Vapor Analysis: to quantify package integrity and internal atmosphere. These test methods may be used to gauge the susceptibility of a device to moisture-related failures triggered by poor sealing processes or internal post-seal outgassing.
- Dye Impregnation and cross-sectional analysis: to detect for moisture ingress pathways in PEMS and other suitable components.
- Decapsulation of PEMS by Fuming Acids.
- Internal Visual Inspection via Optical Microscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): to evaluate the quality of passivation, metallization and other die related components.
- Glassivation Layer Integrity: to assess the structural quality of deposited dielectric films over aluminum metallized devices.
- Bond Strength/Bond Shear: to measure wire bond strengths and evaluate bond strength distributions.
- Die Shear Strength: to determine the integrity of materials and procedures used to attach die or surface mounted passive elements to package headers or other substrates.
- Plasma and Wet Chemical Deprocessing: for sequential unlayering of ICs.
- Die Level Cross-sectional analysis with Field Effect Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM): For high magnification inspection of IC layers.
Construction Analysis does not require disposition as pass/fail criteria inherent to and at times limited by DPA procedures. However, military and commercial standards may be applied to defects to quantify the severity of the condition. Construction Analysis can detect Packaging or IC level concerns that relate to the future reliability of the component.